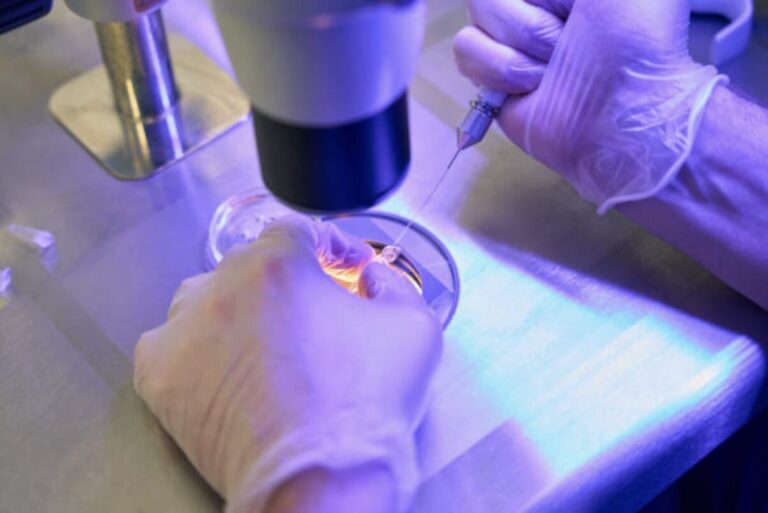
IVF ICSI Explained: The Science Behind Injecting a Single Sperm into an Egg

When most people hear the term IVF, they imagine a single process that works the same way for everyone. In reality, IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) is more like a medical “framework” that can include different techniques depending on what’s preventing pregnancy. One of the most important and widely used techniques inside IVF is ICSI.
ICSI stands for Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection, and it was developed to solve a specific and often misunderstood problem: situations where sperm cannot fertilize the egg naturally, even when sperm is present.
This article breaks down what ICSI is, why it’s used, and how it changes the fertility journey—especially in cases involving male infertility.
What Is ICSI in IVF?
ICSI is a specialized fertilization method performed during IVF. Unlike conventional IVF, where sperm are placed around the egg in a laboratory dish and fertilization occurs naturally, ICSI involves selecting one sperm and injecting it directly into the egg.
This means fertilization is no longer dependent on sperm movement, sperm strength, or the ability of sperm to penetrate the egg’s outer layer. Instead, fertilization is actively assisted by an embryologist using high-precision micromanipulation tools under a microscope.
To explore the full medical overview, you can visit: IVF ICSI.
Why Was ICSI Created?
ICSI became a breakthrough because it directly addressed one of the hardest fertility challenges: severe male factor infertility.
In the past, men with extremely low sperm count or poor sperm quality had limited options. Even IVF couldn’t always help, because IVF still depends on sperm being able to reach and enter the egg on its own.
ICSI changed that by bypassing many natural barriers. As long as viable sperm can be obtained—even in very small numbers—ICSI makes fertilization possible.
ICSI Is Not a Separate Treatment: It’s a Step Within IVF
One common misunderstanding is thinking ICSI is an alternative to IVF. It’s not.
ICSI is a technique within the IVF process. IVF includes:
- hormone stimulation
- egg retrieval
- fertilization (this is where ICSI comes in)
- embryo development
- embryo transfer
So, ICSI doesn’t replace IVF—it modifies the fertilization step in a highly controlled way.
The Meaning of the Term: Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
The name ICSI sounds complex, but it actually describes the procedure precisely:
- Intra = within
- Cytoplasmic = inside the cell fluid of the egg
- Sperm Injection = exactly what happens
In simple terms: one sperm is injected into the inside of the egg.
This technique was introduced in the early 1990s and quickly became one of the most significant advances in reproductive medicine after IVF itself.
Who Typically Needs IVF with ICSI?
ICSI is mainly recommended when there are clear barriers preventing sperm from fertilizing an egg naturally. Some of the most common cases include:
1) Very Low Sperm Count (Severe Oligospermia)
If only a small number of sperm are available, ICSI allows the embryologist to use a single sperm per egg, rather than relying on thousands of sperm being present.
2) Poor Sperm Motility (Severe Asthenospermia)
Even if sperm are alive, they may not swim properly. ICSI removes the need for sperm to travel and penetrate the egg.
3) Abnormal Sperm Shape (Teratospermia)
Sperm morphology can affect fertilization. With ICSI, the embryologist can select the best-looking and most promising sperm for injection.
4) Surgically Retrieved Sperm (Azoospermia)
In some cases, sperm must be retrieved directly from the testes or epididymis through procedures like TESE/TESA. These sperm often cannot fertilize an egg naturally, making ICSI essential.
5) Previous Fertilization Failure
If conventional IVF resulted in low or no fertilization in a previous cycle, ICSI is often recommended for the next attempt.
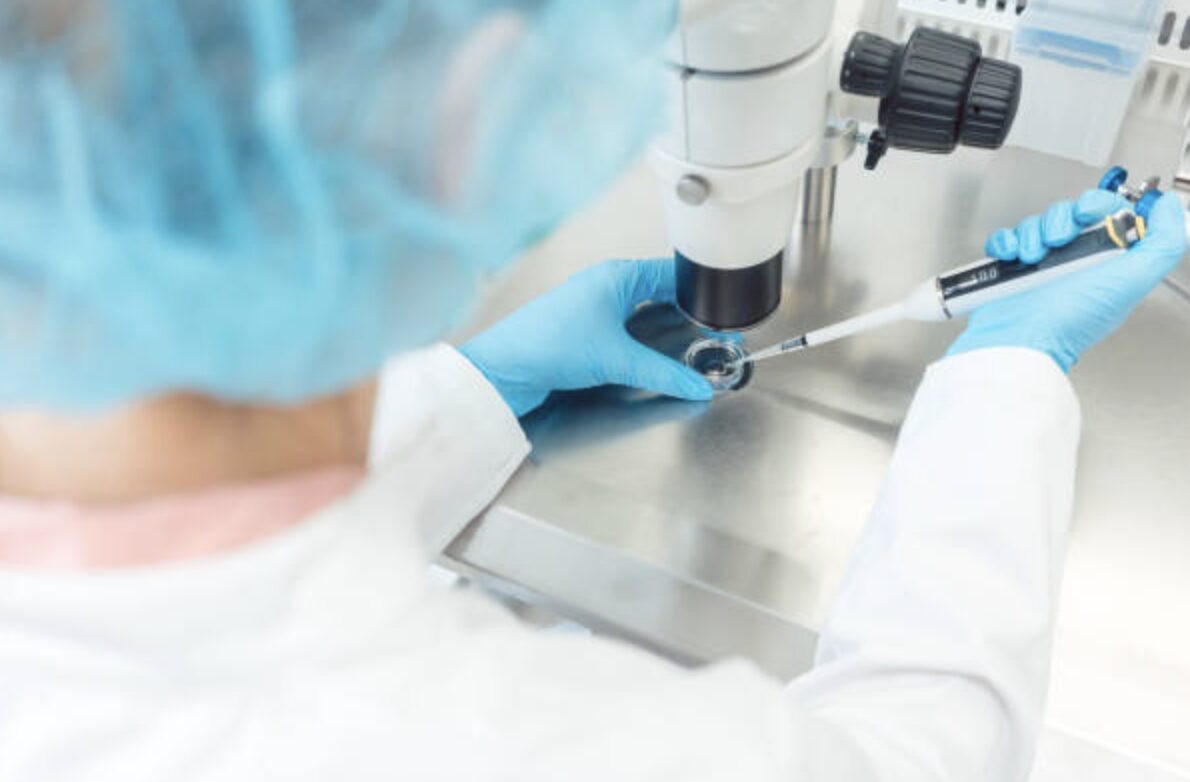
What Actually Happens in the Lab During ICSI?
ICSI is one of the most technical steps in fertility treatment and is performed entirely in the lab.
Here’s what typically happens:
- Eggs are retrieved and assessed for maturity.
- A sperm sample is prepared, and sperm are examined under magnification.
- One sperm is selected for each mature egg.
- The embryologist uses a microneedle to inject the sperm directly into the egg’s cytoplasm.
- Fertilized eggs are then monitored for embryo development over the next several days.
The success of ICSI depends on multiple factors, including egg quality, sperm viability, lab conditions, and embryologist expertise.
What ICSI Can Do—and What It Cannot
It’s important to keep expectations realistic. ICSI improves the chance of fertilization, but it does not guarantee pregnancy.
What ICSI helps with:
- ensuring sperm reaches the inside of the egg
- improving fertilization rates in severe male infertility
- helping when sperm cannot penetrate the egg naturally
What ICSI does not guarantee:
- embryo implantation
- pregnancy continuation
- live birth outcome
Pregnancy depends on the embryo’s genetic health, uterine receptivity, and many medical and lifestyle factors beyond fertilization.
Why ICSI Matters in Modern Fertility Medicine
ICSI didn’t just improve outcomes—it changed what was possible.
It has enabled parenthood for men who previously had almost no fertility options. It also supports other advanced fertility tools, including Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT), since ICSI reduces the risk of contamination by additional sperm during fertilization.
In many clinics today, IVF with ICSI is not rare—it’s routine, particularly when male fertility factors are involved.
To explore more reproductive health and treatment resources, you can visit Liv Hospital.
Final Thoughts
IVF ICSI is one of the most important innovations in assisted reproduction because it tackles the fertilization barrier directly. By injecting a single sperm into an egg, ICSI gives many couples a realistic path forward even when sperm count, motility, or morphology are severely affected.
And because fertility is influenced by the whole body—not just reproductive organs—many people also focus on lifestyle improvements like stress management, nutrition, sleep, and daily movement while undergoing treatment. For wellness content and lifestyle guidance, you can explore live and feel.