Software development is a challenging task that requires proper management of the workflow with constant monitoring. Even though there are numerous methods to engage in software development, Kanban is one of the most popular methods. Kanban helps to bring consistency to the workflow required in software development. Its particular focus on visualizations is beneficial to understand it further. Often the Kanban approach is wrongly assumed to create a Kanban board only. Instead, it houses an entire system to ensure that the approach is correct. In this post, we will figure out how to exactly use Kanban for software development.
1. Set The Kanban Board
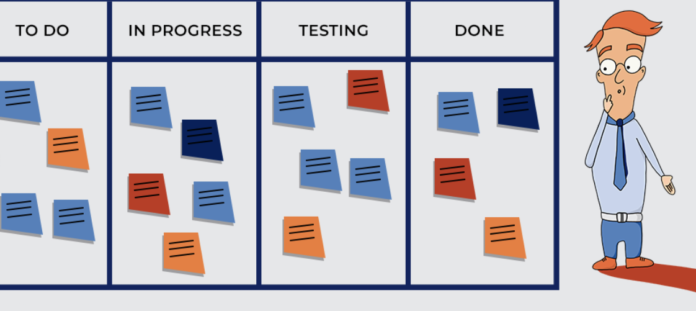
Firstly, you need to create a Kanban board to handle the different stages of software development. Next, you need to create separate lists on this board and give them a title. Finally, consider labeling the lists with tags such as backlog, business requirement, ready for review or coding, coding, code review, done and more. It is a good idea to discuss with the team members to decide on the correct tags for the columns.
While creating a list or a column on the Kanban board, it is crucial to remember only some things that share the same priority. Therefore, you should further arrange columns based on priority to ensure you focus on the element that matters most. The first step helps you meet the core principle of Kanban, which is visualization. Also, after you have created the Kanban board, add the tasks in the cards and assign them to the respective team members.
2. Limit Work In Progress
The second core principle of Kanban is limit. It is crucial to limit the tasks for different members to maximize efficiency. Limits ensure that the team members focus on one task rather than juggling multiple jobs daily, reducing efficiency. The limiting feature of Kanban comes through the PULL system, which refers to work-in-progress limits.
While lowering the limit to increase the speed of progress, you need to be careful because there is a critical point associated with it. If you have a higher limit, the cycle times get longer and vice versa. However, if the limit is too low, the performance of the work takes a negative toll. Also, after setting the limit, it is crucial to ensure you do not exceed it, which defeats the whole purpose of it. You can use the initial experiences’ results to set the correct limit.
3. Plan
The third step of Kanban focuses on optimization, which is achievable through proper planning. Planning in Kanban is different from other methods because it is all about positioning the cards and columns in the correct order to decide the priority of the tasks. For example, you placed a McDVoice survey creation form in the topmost column. In that case, you need to complete this task before shifting to another job which might involve reviewing the responses to the DGCustomerFirst surveys.
However, even when planning, it is crucial to have a proper estimation to complete the task, if not a proper deadline. Also, you should schedule a task so that a dependency is maintained to ensure maximum focus on a particular job.
4. Focus On Collaboration
Kanban works in the agile framework, which is about continuous software improvement. It primarily runs on a feedback cycle to achieve it. Working towards improving software requires robust collaboration between the team members. You can use the Kanban board along with an email to create a sync between both the internal and external stakeholders. Kanban makes it possible to collaborate by allowing team members to create cards within the board concerning tasks.
The Benefits Of Kanban
The first benefit of Kanban is that it helps visualize the entire workflow, making it easier to make changes as per requirement. Also, it accelerates software delivery by helping the members manage the priorities and needs of different work. Because Kanban ensures focus on one task at a time, it incredibly increases the entire team’s productivity to deliver high-quality software. Furthermore, it reduces the work burden of the team members with efficient distribution of the work. It is an easy-to-use approach which is market-flexible and helps improve teamwork. Lastly, it promotes experimentation and collaboration, which is necessary for developing software.